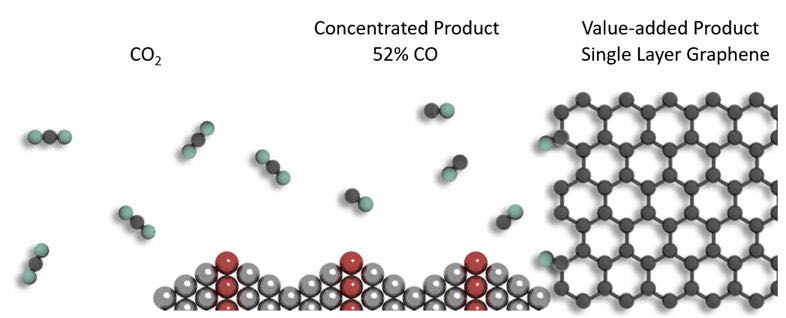
The gaseous product concentration in direct electrochemical CO2 reduction is usually hurdled by the electrode’s Faradaic efficiency, current density, and inevitable mixing with the unreacted CO2. A concentrated gaseous product with high purity will greatly lower the barrier for large-scale CO2 fixation and follow-up industrial usage. Here, we developed a pneumatic trough setup to collect the CO2 reduction product from a precisely engineered nanotwinned electrocatalyst, without using ion-exchange membrane. The silver catalyst’s twin boundary density can be tuned from 0.3 to 1.5 × 104 cm−1. With the lengthy and winding twin boundaries, this catalyst exhibits a Faradaic efficiency up to 92% at −1.0 V and a turnover frequency of 127 s−1 in converting CO2 to CO. Through a tandem electrochemical-CVD system, we successfully produced CO with a volume percentage of up to 52%, and further transformed it into single layer graphene film.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-22428-1
