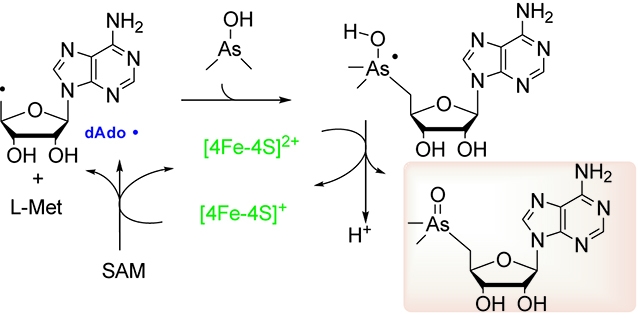
Arsenosugars are a group of arsenic‐containing ribosides that are found predominantly in marine algae but also in terrestrial organisms. It has long been proposed that arsenosugar biosynthesis involves a key intermediate 5'‐deoxy‐5'‐dimethylarsinoyl‐adenosine (DDMAA), but how DDMAA is produced remains largely elusive. In this study, we report characterization of ArsS as a DDMAA synthase, which catalyzes a radical S‐adenosylmethionine (SAM)‐mediated alkylation (adenosylation) of dimethylarsenite (DMAs III ) to produce DDMAA. We show this radical‐mediated reaction is redox neutral, and multiple turnover can be achieved without external reductant. Subsequent phylogenomic and biochemical analyses revealed that DDMAA synthases are widespread in distinct bacterial phyla with similar catalytic efficiencies, and these enzymes likely have originated from cyanobacteria. This study not only reveals a key step in arsenosugar biosynthesis but also a new paradigm in radical SAM chemistry, highlighting the remarkable catalytic diversity of this superfamily of enzymes.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202015177
